
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
Menu
Home » Everything You Need To Know About Galvanised Angle
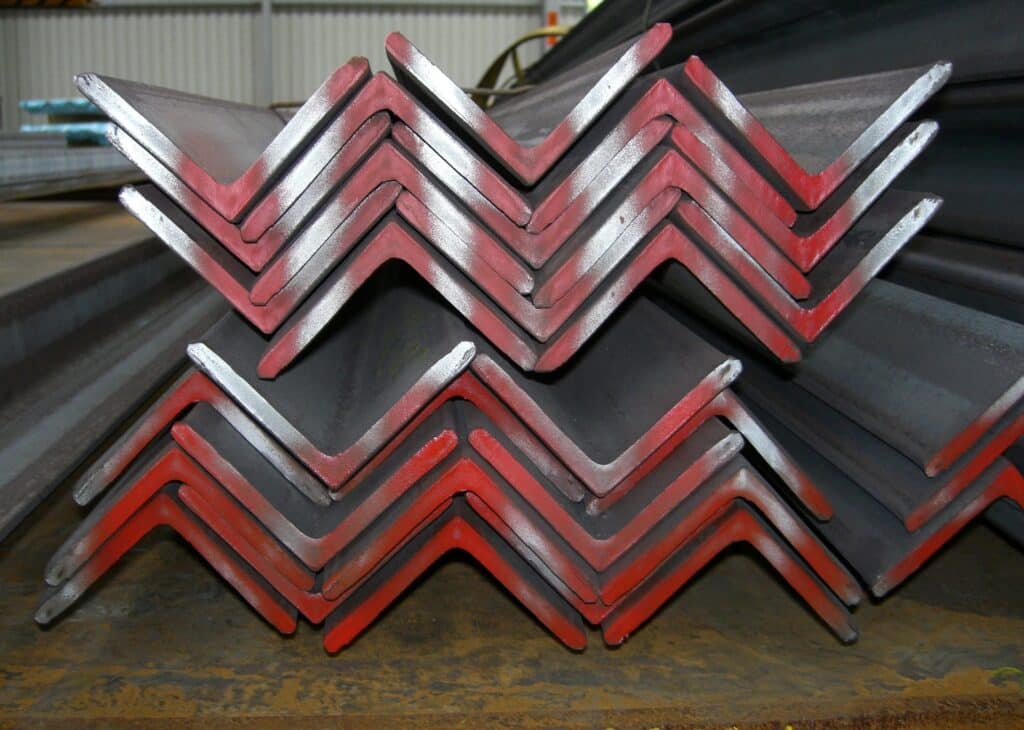

We have recently added galvanised steel angle to our ever-expanding range of products. This guide has been made to answer any questions that you may have before choosing this material. We also recommend that you check out our blogs What Can Aluminium Angle Be Used For? and Mild Steel Angle Iron for more information on angle products
We hope that you find this simple guide informative and helpful.
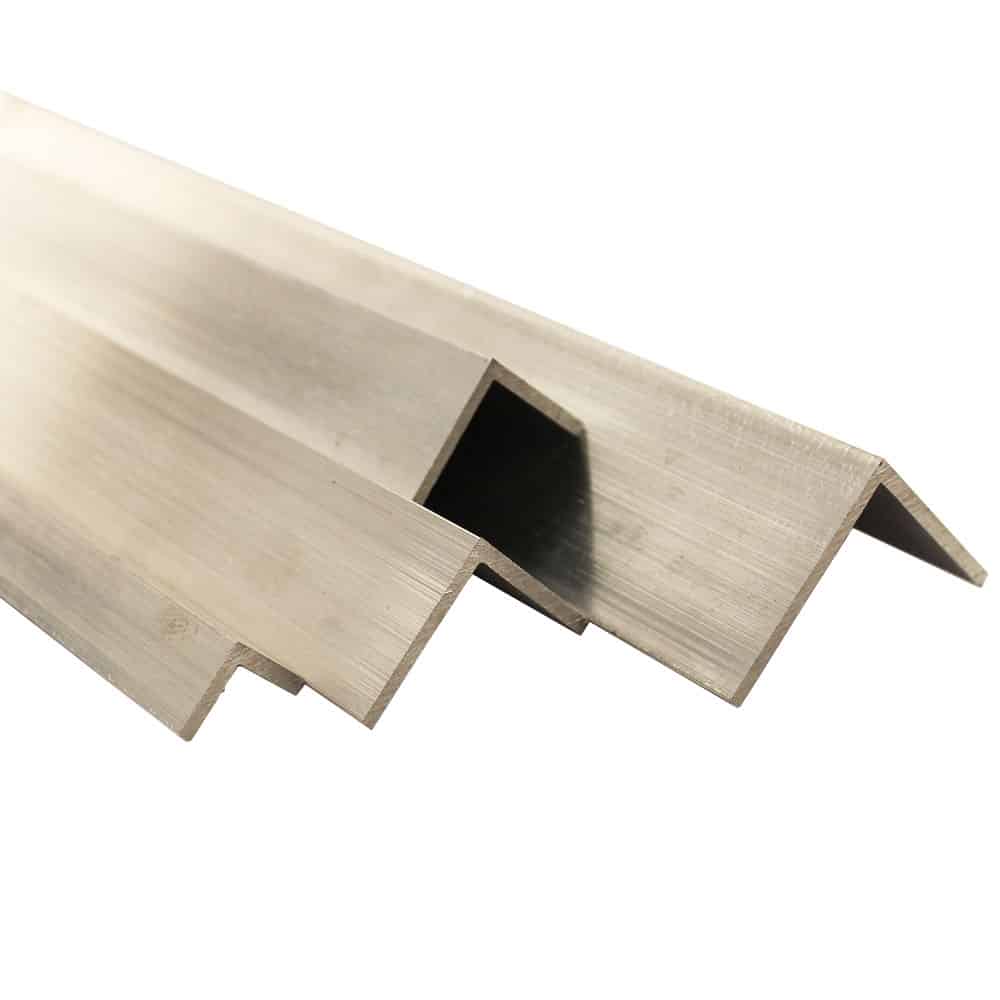

Galvanised steel is great for outdoor construction and other applications where the steel will be exposed to the elements. Galvanised steel angles are available in a variety of sizes and grades to meet different needs.
Angle trim, also known as corner trim or angle iron, is a type of trim used to finish and protect the edges of drywall or plaster walls and ceilings. It is made of metal, usually galvanised steel, plain steel or aluminium, and is used to create a neat, finished edge where two walls or a wall and ceiling meet. Angle trim is also used to reinforce the corners of a wall, helping to prevent cracking and damage. It is typically installed by nailing or screwing it to the wall or ceiling, then covering it with joint compound and smoothing it out to create a seamless finish.
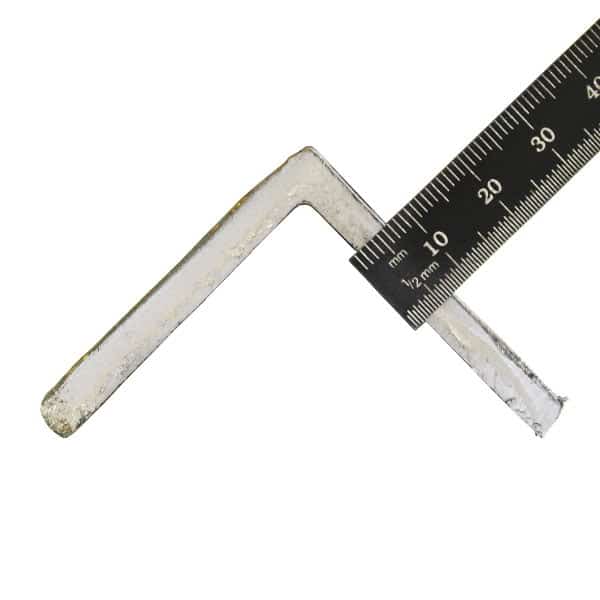
Angle iron is typically measured by its legs, which are the two sides that form the angle. The legs are measured in inches or millimetres, and the thickness of the angle iron is also typically measured in inches or millimetres. Additionally, the angle of the angle iron, typically measured in degrees, can also be specified. For example, a common specification for angle iron might be “2 x 2 x 1/4 x 90 degrees,” which indicates that the legs of the angle are 2 inches by 2 inches, the thickness of the angle iron is 1/4 inch, and the angle of the angle iron is 90 degrees.
We always use millimetres. Our our angle may measure something like ’20 x 20 x 3mm’. This is 3mm thick with 20mm legs.
To cut angle iron, you can use a variety of tools including a metal cutting saw, a hacksaw, a cutoff wheel, or a plasma cutter. Each tool has its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific cutting needs and the resources available.
It is important to use the appropriate safety equipment and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the tool you choose.
Angle iron is a strong, durable material that is commonly used in construction and fabrication. Its strength comes from its L-shaped cross-section, which provides structural support and stability. Additionally, angle iron is made of steel, which is known for its high strength and durability. The thickness of the steel and size of the angle iron also affect its strength. It is also commonly used for corner reinforcements, bracing, and supports in structures.
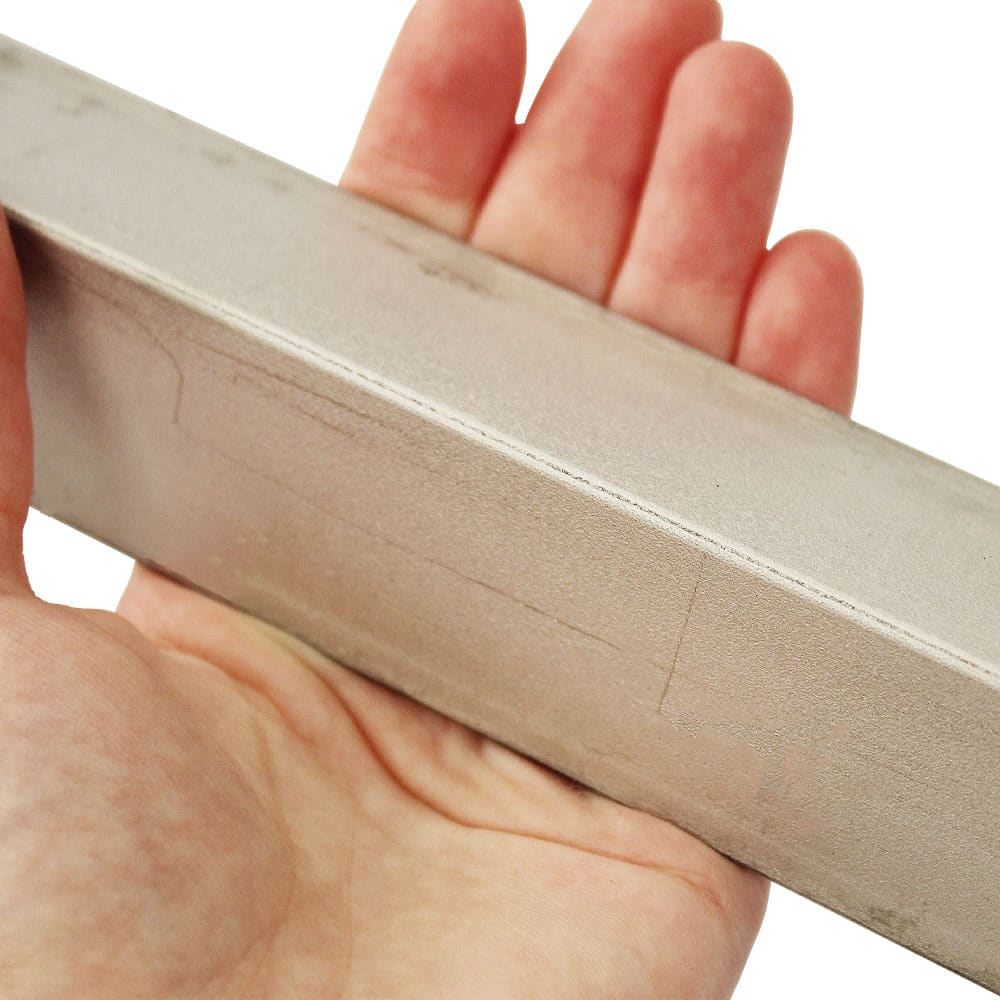

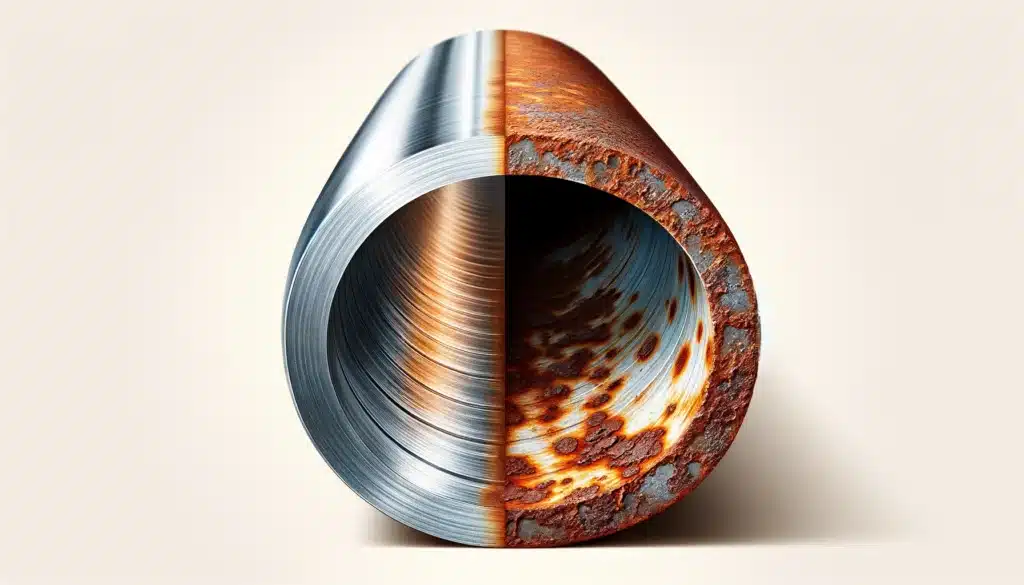
Galvanised steel is steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from rust and corrosion. The zinc coating acts as a barrier that prevents oxygen and water from reaching the steel, which slows down the rusting process. However, it is not completely rust-proof and over time, the zinc coating can wear away, exposing the steel to the elements and allowing rust to form. In addition, galvanised steel can still corrode if it is exposed to certain chemicals or if the zinc coating is damaged.
Yes, galvanised steel can bend, but it may be more brittle and less ductile than uncoated steel. The galvanization process, which involves coating the steel in zinc, can make the steel more prone to cracking or breaking when bent. The thickness and grade of the steel can also affect its ability to bend.
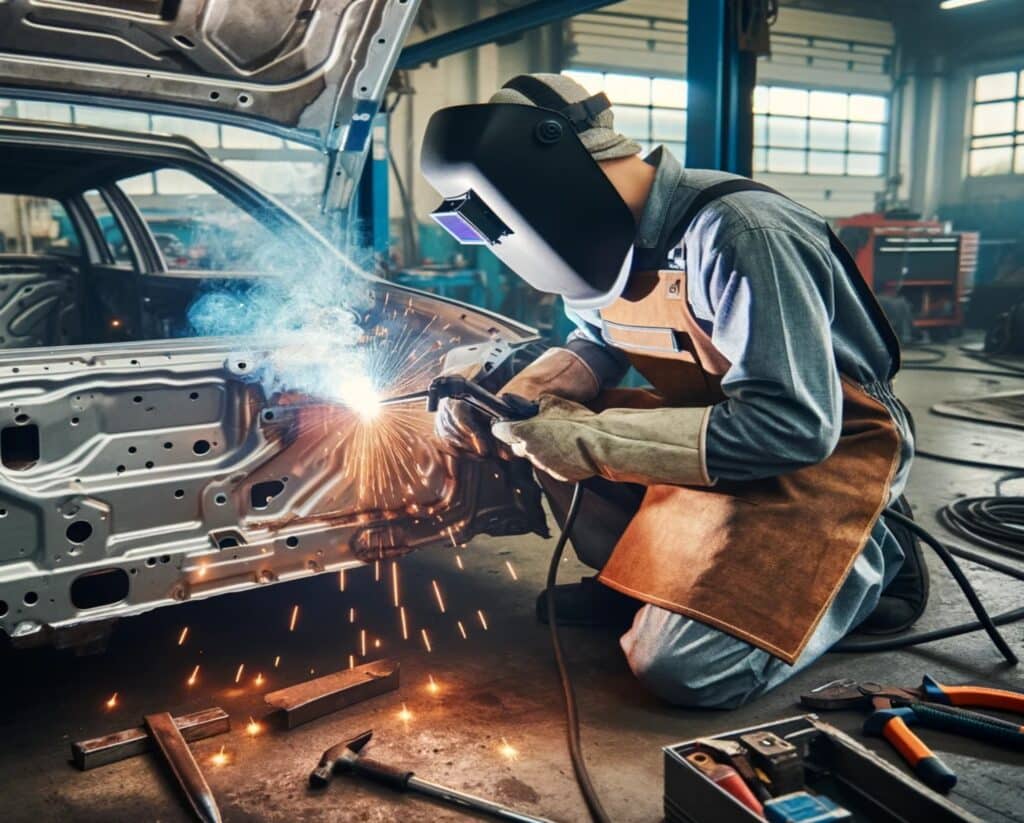
Yes, you can weld galvanised steel, but it does require some special considerations. Galvanised steel is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. When welding, the heat from the welding process can cause the zinc coating to vaporize, creating zinc oxide fumes that can be hazardous to inhale. To minimize this, it is recommended to use a lower heat setting on the welding torch and to use proper ventilation to disperse the fumes. Additionally, it is also recommended to use a welding wire specifically designed for welding galvanised steel.
Yes, you can paint galvanised steel, but it does require some preparation to ensure proper adhesion. Before painting, the galvanised surface should be cleaned thoroughly to remove any oils, dirt, or other contaminants that may be present. This can be done using a degreaser or a solution of water and detergent.
It is also recommended to lightly sand the surface to help create a better bond between the paint and the galvanised surface. After cleaning and sanding, the surface should be rinsed off thoroughly and left to dry completely before applying a coat of primer specifically designed for use on galvanised steel. After the primer has dried, you can apply your desired paint.

Galvanised steel has a relatively low heat resistance compared to other types of steel. The zinc coating on the surface of the steel has a melting point of around 787 °F (420 °C). When exposed to temperatures above this, the zinc coating can start to melt and lose its protective properties. In addition, the heat from welding or other high-temperature processes can cause the zinc coating to vaporize, releasing zinc oxide fumes.
It’s important to note that the heat resistance of galvanised steel also depends on the thickness of the zinc coating. Thicker coatings will have a higher heat resistance than thinner coatings.
For high-temperature applications, it’s recommended to use other types of steel or coatings that can withstand higher temperatures. In case of high temperature application, it is always recommended to consult with us first or with an expert metallurgist.
Galvanised steel is machinable, but it may be more difficult to work with than uncoated steel due to the zinc coating. The zinc coating can cause adhesion issues and increase cutting resistance. Additionally, the zinc fumes generated during machining can be harmful to inhale, so proper ventilation and respiratory protection should be used. It is also recommended to use high-speed steel or carbide cutting tools, as they are more durable than regular steel tools and can withstand the increased cutting resistance.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project.
Please also check out the other articles in our helpful guide series. We have written about aluminium sheeting and checker plate recently to name but two of our articles.
We are also proud to sell this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us.







Speciality Metals
Unit 1, Farrell Street, Warrington,
Cheshire, WA1 2WW, United Kingdom
Quick Links
Payment Options
