
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
Home » The Comprehensive Guide to Metal Adhesives: From Epoxies to Welds
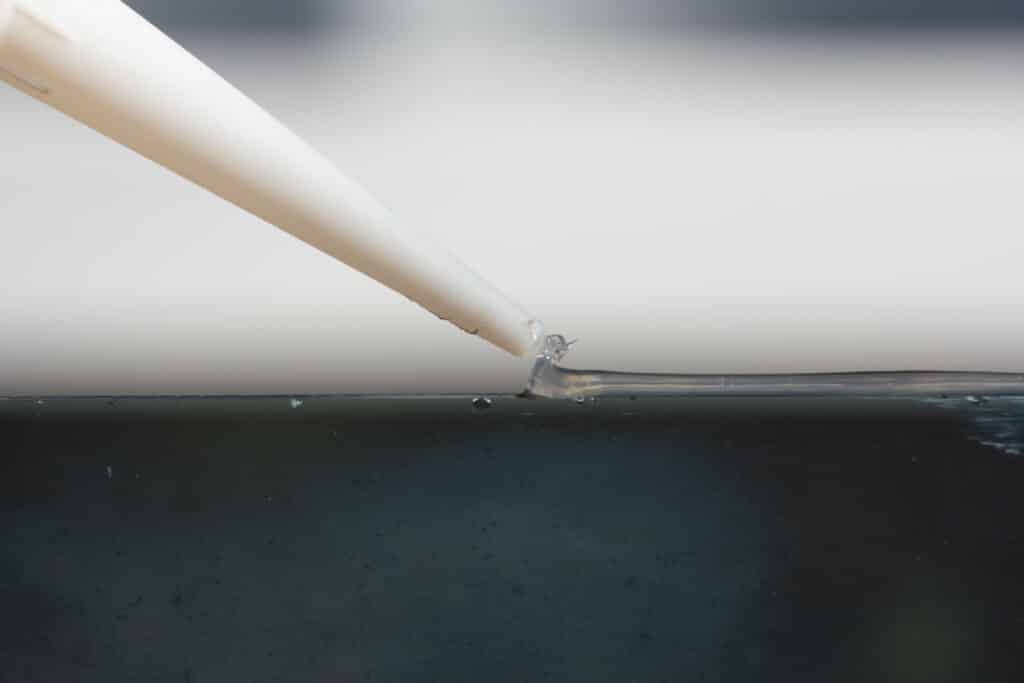

When it comes to adhering two metals, the process can be significantly different from bonding other materials. Metals present unique challenges and also offer a wide range of options for adherence, ranging from chemical adhesives to physical methods like welding. The vast world of ‘metal adhesives’ encompasses a spectrum of products, each with its specific benefits and applications. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into these metal adhesives to provide insight into the best choice for your project.
Before delving into the types of metal adhesives, let’s understand why there’s a need for specialised adhesives for metals. Metal substrates are non-porous and might have a smooth or rough surface. This makes them relatively challenging for certain adhesives to grip. Moreover, metals are susceptible to temperature fluctuations, oxidation, and other environmental factors, requiring adhesives that can withstand these variables.
1. Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins are perhaps the most common type of metal adhesive and are used in numerous applications. Here’s what makes them stand out:
2. Cyanoacrylates
Often known as ‘super glues,’ cyanoacrylates provide quick bonding solutions.
3. Anaerobics
Anaerobic adhesives cure in the absence of air. They’re commonly used for sealing threads and preventing corrosion.
4. Polyurethanes
A versatile option, polyurethanes offer excellent flexibility and bond strength.
5. Acrylic Adhesives
These are excellent alternatives to epoxies and cyanoacrylates and provide robust bonding for metals.
Welding is a classic method to join metals. Unlike chemical adhesives, welding fuses metals together by melting the surfaces.

Versatility in Material Compatibility: Adhesives can bond a variety of metals, including those that are challenging to weld. They can also bond dissimilar metals, which can be complex or impossible to achieve with welding.
No Thermal Distortion: Welding introduces heat, which can cause warping or distortion, especially in thin metals. Adhesives bond without such high-temperature inputs, maintaining the original shape and integrity of the components.
Uniform Stress Distribution: Welded joints can have localised stress points, while adhesively bonded joints distribute stress uniformly across the bond line, leading to potentially longer-lasting bonds under certain conditions.
Surface Preservation: Welding can discolor metals or create splatter. Metal adhesives maintain the aesthetics and finish of the surface, making them preferable for visible joints or applications where appearance matters.
No Need for Holes: Welding can sometimes necessitate drilling holes (as in spot welding), weakening the material. Adhesives don’t require such modifications.
Reduced Labor and Equipment Costs: Welding requires skilled labor and specialised equipment, which can be costly. While some adhesives also need special equipment, many can be applied with simple tools, reducing overall costs.
Enhanced Flexibility: Certain adhesives can absorb shocks and vibrations better than welded joints, providing a degree of flexibility that’s beneficial in dynamic environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Adhesive bonding can create a seal, preventing moisture and air from reaching the metal, thus offering protection against corrosion at the bond line. In contrast, welding can sometimes introduce sites for corrosion if not done or treated correctly.
Safety: Welding involves the risk of burns, fire, exposure to harmful gases, and eye damage due to the intense light. Using adhesives can be a safer process.
Weight Reduction: Adhesives can be lighter than the additional metal used to create a weld, leading to weight savings – crucial in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Sealing: Apart from bonding, adhesives also provide a seal against air and moisture, which can be beneficial for applications requiring both bonding and sealing.
No Post-Processing: Welded joints often require grinding or smoothing post-welding. Adhesive bonds, when applied correctly, may not require any such post-application processing.

Limited High-Temperature Resistance: While some adhesives can withstand elevated temperatures, many may degrade or lose their bonding strength when exposed to high heat, making them unsuitable for applications with extreme temperature requirements.
Surface Preparation: Adhesive bonding often requires thorough surface preparation, such as cleaning, priming, or roughening, to achieve optimal bond strength. This can add to the overall process time.
Curing Time: Many adhesives require a specific curing time to achieve full strength, which can delay further processing or testing of the bonded assembly. In contrast, welded joints are often ready for use almost immediately.
Long-Term Durability Concerns: Some adhesives may degrade over time due to environmental factors such as UV exposure, moisture, or chemicals. This can impact the longevity of the bond.
Limited Gap-Filling Abilities: While certain adhesives can bridge small gaps between components, they aren’t always suitable for larger gaps. Welding, on the other hand, can fill gaps using additional filler material.
Strength Limitations: Welded joints, in some cases, can provide higher mechanical strength than adhesive bonds, especially in load-bearing applications.
Chemical Exposure: Some adhesives release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the curing process. Additionally, exposure to certain chemicals or solvents can weaken or dissolve the adhesive bond.
Storage and Shelf Life: Adhesives often have specific storage requirements and a defined shelf life, beyond which they may not perform optimally.
Skill Requirement: Though different from welding, achieving a strong and durable adhesive bond requires knowledge of the adhesive’s properties, correct application techniques, and understanding of curing processes.
Difficulty in Disassembly: If parts need to be disassembled for maintenance or repair, breaking an adhesive bond without damaging the components can be challenging. Welded components, depending on the type of weld, can sometimes be more straightforward to separate using cutting or grinding.
Cost: High-performance adhesives, especially those developed for specific industrial applications, can be expensive.
Potential for Bond Line Thickening: If too much adhesive is applied, or if it’s not uniformly spread, it can lead to thickening of the bond line, which may compromise joint aesthetics and performance.
Metal adhesives are a vast and varied domain, offering solutions that range from quick-set super glues to the time-tested reliability of welding. The right adhesive not only ensures the durability and strength of a bond but also its longevity. Whether you’re working on a DIY project at home, an industrial-scale assembly, or intricate jewelry work, understanding the nuances of metal adhesives can make all the difference in the outcome. Remember, the bond is only as strong as the adhesive that forms it.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project.
Please also check out the other articles in our helpful guide series. We have written about ‘Understanding Corrosion: The Biggest Enemy of Metals‘ and ‘What is TIG Welding and How It Can Be Used for Metal Materials?‘ recently so why not check them out?
We are also proud to sell this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us.












Speciality Metals
Unit 1, Farrell Street, Warrington,
Cheshire, WA1 2WW, United Kingdom
Quick Links
Payment Options
