- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
Menu
Home » Galvanised Steel vs. Aluminium – The Pros and Cons
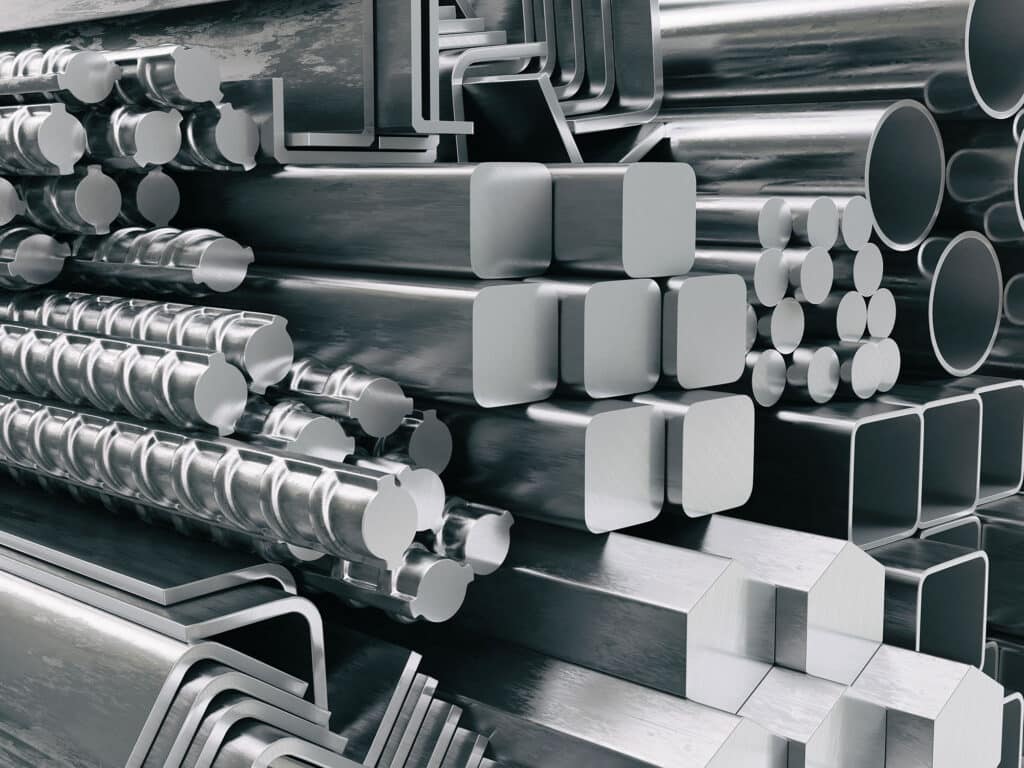
When it comes to constructing a building, choosing the right material is crucial. Two popular materials that are used are galvanised steel and aluminium. Both have their own unique features, advantages, and disadvantages.
So, which one should you choose? In this blog post, we’ll compare galvanised steel and aluminium and highlight their respective benefits and drawbacks, helping you to make an informed choice.
Let’s go…
As far as strength is concerned, there is no doubt on the fact that galvanised steel is stronger than other steel options. In addition to being robust and durable, galvanised steel can also withstand extreme weather conditions without deteriorating. In contrast, aluminium is weaker in comparison to steel, but it still has a great deal of durability. There is a possibility of increasing the strength of aluminium by combining it with other materials, but the amount of money spent on that will increase as well.
On the other hand, if you break down the weight-to-strength ratio, aluminum comes out on top. Due to this, aluminium is a better choice for projects that require lightweight materials, whereas steel is a better choice for heavy-duty applications.
In certain construction projects, aluminium can be an ideal material due to its lightweight characteristics. There are many lightweight structures made of carbon fiber, including airplanes, cars, and other vehicles. However, galvanised steel is clearly the winner if weight is not your primary concern. It’s heavier but provides more stability, especially in places where winds can be strong.
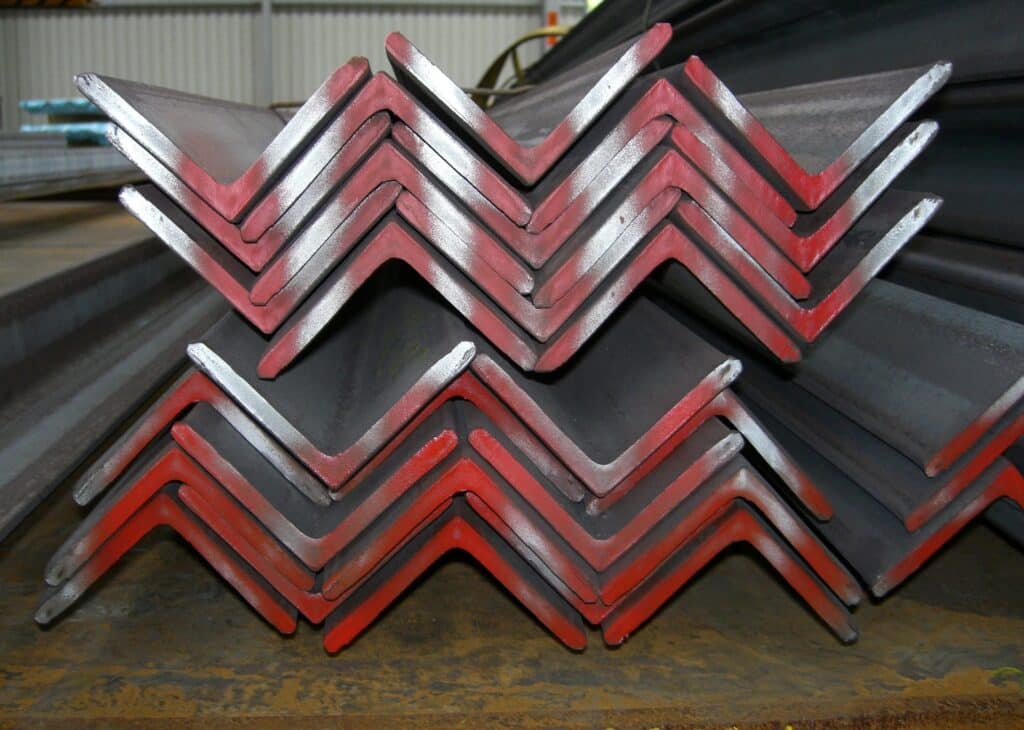

A zinc coating is applied during the manufacturing process to galvanised steel in order to make it corrosion resistant. Zinc coatings can provide protection for several decades. Despite the fact that aluminum does not corrode, it can corrode if it comes into contact with other metals.
The heat transfer efficiency of aluminium is over four times that of steel. Metal particles are held together by strong metallic bonds. Aluminium efficiently conducts heat because the free electronics within it are free to move around. Aluminium is widely used in heatsinks on electrical appliances. For this reason, most modern mobile phones and laptops are made of aluminium. Additionally, it is used in car radiators since it can withstand extreme temperatures without corroding. It is a highly cost-effective and versatile heat transfer material that can replace steel in many applications.
The thermal conductivity of galvanized steel is moderate to high, making it an efficient heat conductor. As a result of its metallic composition and zinc coating, galvanized steel allows heat to transfer relatively quickly through its structure. Applications that require heat dissipation or transfer can benefit from galvanized steel’s thermal conductivity, such as heat exchangers, radiators, and HVAC systems. However, it’s important to consider the potential for heat loss or gain in certain situations, as galvanized steel’s thermal conductivity may result in increased energy usage or heat transfer in environments with extreme temperatures. Proper insulation or additional measures may be necessary to manage thermal conductivity effectively in such cases.
How often should the metal be cut and reformed to fit the product? The process of welding galvanized steel is time-consuming and difficult. Because toxic fumes are released, strict safety codes must be followed.
Aluminium is a much more malleable metal. It has an aluminium oxide surface coating, high thermal conductivity, and low melting temperature, and the material doesn’t change as the temperature meets its melting point.
We have released several articles on welding with metals that may be of assistance. Subjects include TIG welding and the fundamentals of welding sheet metal.
Cost is a crucial factor in any building project. Galvanised steel is the most cost-effective option, making it a popular choice for building construction. Aluminium is a more expensive material than galvanised steel, but it’s also more lightweight and durable.
Despite its higher cost than aluminium, galvanised steel is suitable for a number of projects because of its strength. In large infrastructure projects, such as bridges and roads, girders, construction supports, and frames, its long life cycle and noncorrosive properties make it the preferred choice.
The lightness, malleability, and greater thermal conductivity of aluminum make it ideal for architectural applications such as window frames, balcony railings, roofing sheets, interior ceiling panels, paneling, and cladding.
Moreover, aluminium can also be recycled 100% without losing any of its original properties and with a 5% reduction in energy consumption. Construction finishing replacement cycles are particularly relevant when considering this.















Aluminium and galvanised steel each have their own advantages and disadvantages, making it difficult to decide between them. Galvanized steel is the best choice if you are concerned about strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. If you need a lightweight material that can withstand the elements, aluminum is the best choice. Ultimately, it depends on your project’s specific needs, the location, and your budget.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project.
Please also check out the other articles in our helpful guide series. We have written about aluminium sheeting and checker plate recently to name but two of our articles.
We are also proud to sell this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us.

Speciality Metals
Unit 1, Farrell Street, Warrington,
Cheshire, WA1 2WW, United Kingdom
Quick Links
Payment Options
