
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
Home » Is Mild Steel Magnetic? Varieties and Magnetism Explained

Mild steel is a popular choice in the construction and manufacturing sectors due to its malleability, durability, and affordability.
A frequently asked question regarding this material is: “Is all mild steel magnetic?” To fully answer this, we’ll delve into the properties of mild steel, its various types, and its magnetic attributes.
Let’s get into it…
It is important to understand why some metals are magnetic and others are not before discussing the magnetism of mild steel. The motion of electrons, particularly their spin, causes magnetism.
An unpaired electron in a metal like iron aligns with its spin in the presence of a magnetic field, making it attracted to magnets.
Compared to high carbon steel, mild steel has a lower carbon content (typically 0.05–0.30%) which makes it more malleable and ductile. Its magnetic properties are due to the iron content, which is the predominant element in mild steel.
The answer is yes, mild steel is magnetic. Steel itself is magnetic due to its high iron content, which aligns the unpaired electrons in the atoms when exposed to a magnetic field. While the strength of mild steel’s magnetism can vary based on its exact composition and processing, this property remains consistent across most types.
Mild steel, known for its versatility and formability, is not a singular entity. As a result, it comes in a variety of grades, each tailored to a specific purpose based on its chemical composition and properties. Below is a breakdown of the key types of mild steel, ensuring you choose the right one for your project.
Grade 250 (G250) Steel:
Grade 350 (G350) Steel:
Grade A Steel:
EN1A (220M07):
EN3B (070M20):
EN8 (080M40):
S275 & S275JR:
S355:
Ensure the success of your project by understanding the specific grades of mild steel. Building a complex structure or crafting a specific part requires balancing formability, strength, weldability, and corrosion resistance. If in doubt, consult metallurgists or experts, and remember that the grade you choose will have a significant effect on the product’s longevity and performance.
Let’s explore the different forms of mild steel that we stock and how their magnetism comes into play:

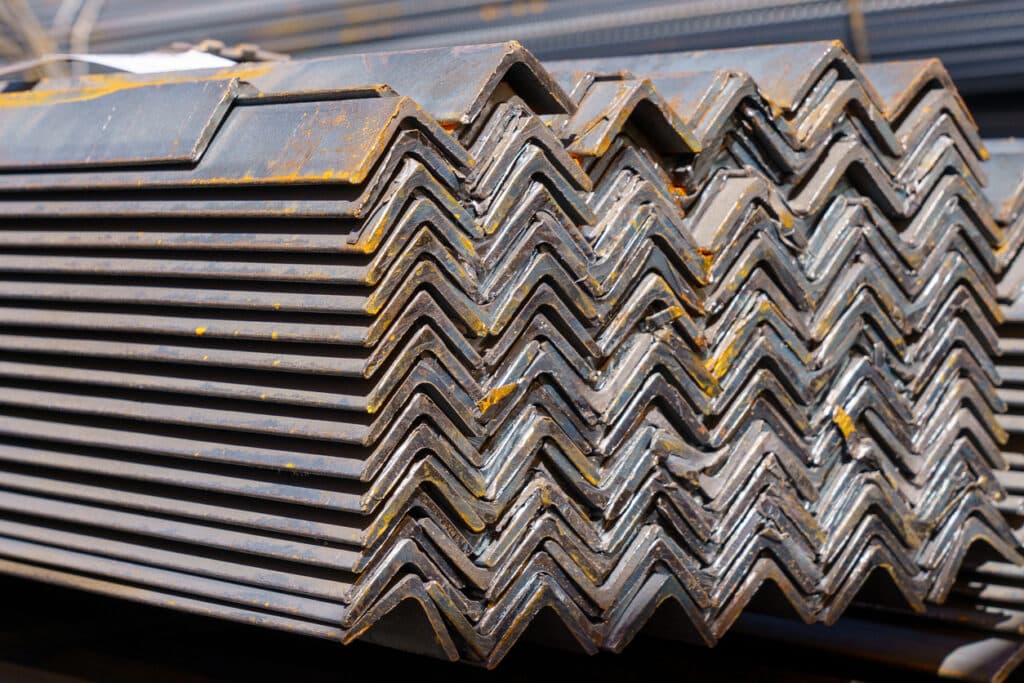
As the name suggests, this is an L-shaped product used primarily in construction and fabrication. It retains the magnetic properties inherent to mild steel.
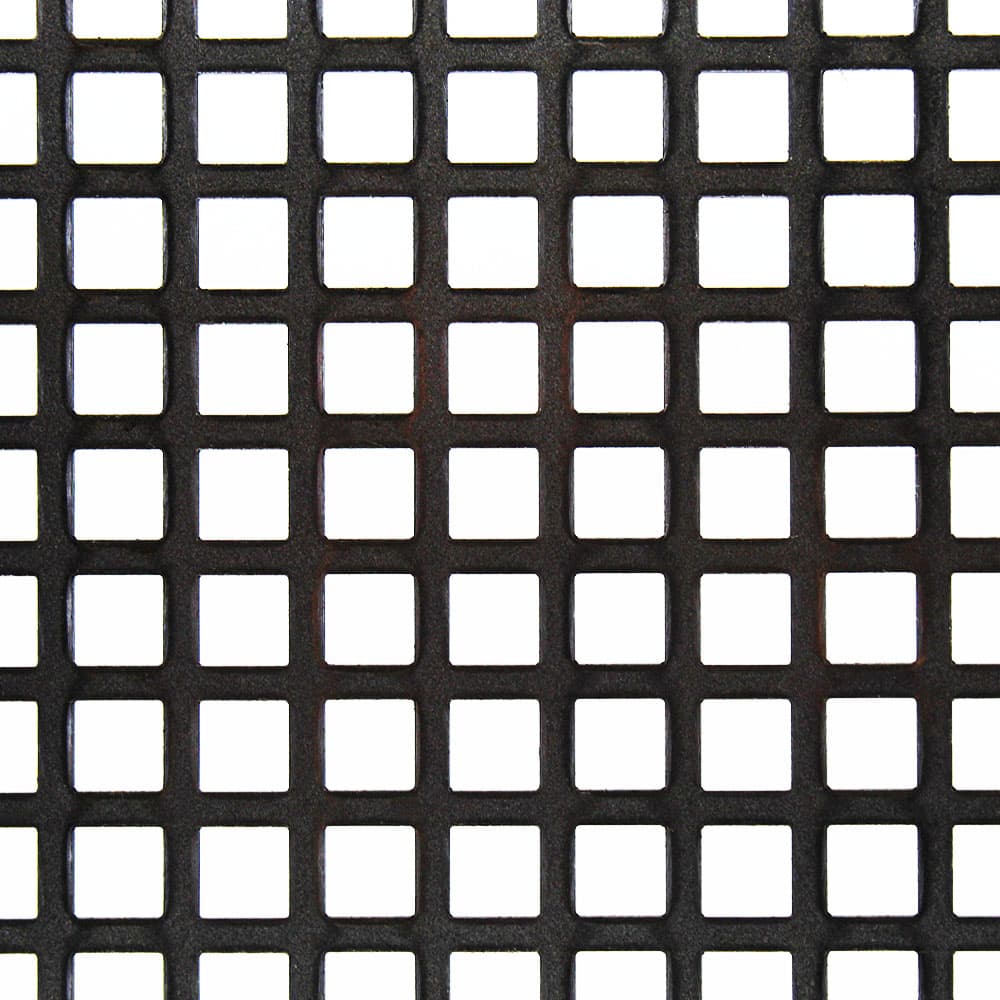
This form of mild steel has holes punched, drilled, or stamped into it, creating a patterned sheet. The perforations don’t alter the fundamental magnetic properties of the steel.

Circular hollow sections used in construction, transportation, and other sectors. The fact that it’s hollow doesn’t interfere with its magnetic properties.
A thin, flat piece of steel used in myriad applications. Its magnetic attributes are similar to other forms of mild steel.


These are flat, rectangular bars of mild steel. Their broad, flat surfaces are excellent for magnetic applications.
Also known as square or rectangular hollow sections, they are primarily used in construction. Like round tubes, their hollow nature doesn’t impact their magnetic properties.

The magnetic properties of mild steel make it a versatile and vital material in many industries. Perforated metal, sheet, angle, round tube, flat bar, and box sections all maintain consistent magnetic properties, making them suitable for applications requiring magnetic repulsion.
Whether you’re designing a product or working on a construction project, our extensive selection of mild steel options can meet your needs. Browse our inventory to find the perfect fit for your requirements, and remember that mild steel’s magnetic properties add functionality, testing simplicity, and versatility.
Mild steel’s magnetic nature has several practical implications. Electromagnets, transformers, and motor cores frequently use it. Its ability to become magnetized and demagnetized quickly makes mild steel invaluable in these applications.
Additionally, mild steel’s magnetism makes testing and quality assurance easier. A simple magnet test can be used to distinguish mild steel from other non-magnetic metals.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project.
Please also check out the other articles in our helpful guide series. We have written about aluminium sheeting and checker plate recently to name but two of our articles.
We are also proud to sell this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us.














Speciality Metals
Unit 1, Farrell Street, Warrington,
Cheshire, WA1 2WW, United Kingdom
Quick Links
Payment Options
