
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
- Massive Range
- FREE UK Delivery
- Rapid Dispatch
Home » How to Choose the Right Fasteners for Corrosive Environments
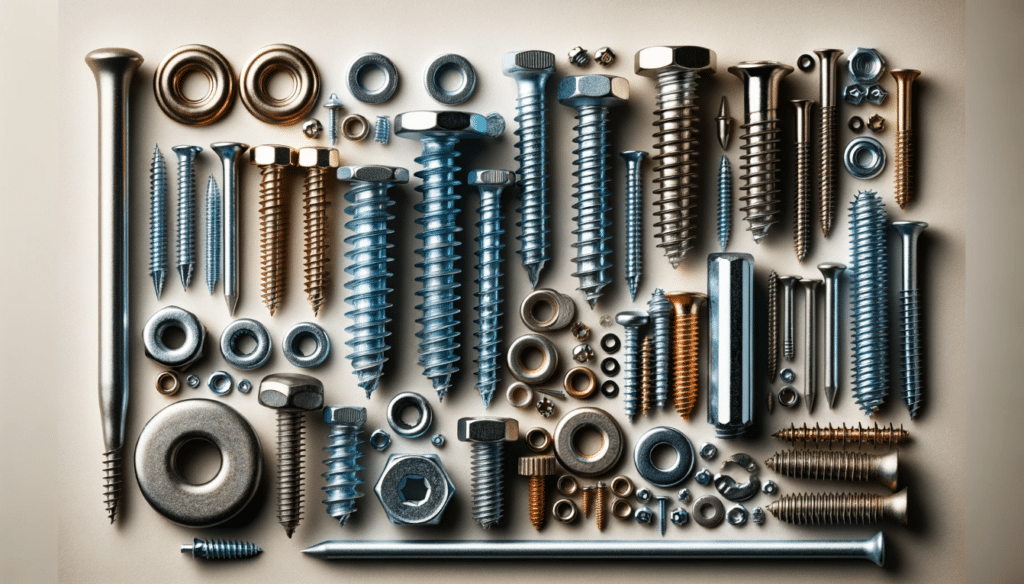
When selecting fasteners for any application, the environment in which they will be used is a critical factor. Corrosive environments make this decision even more critical, since the wrong choice can cause premature failure, safety risks, and high maintenance costs. You can make informed decisions if you know how corrosion occurs and which materials and coatings provide the best resistance. Here are the essential considerations to ensure durability and reliability when choosing fasteners for corrosive environments.
A corrosive environment is one that promotes the deterioration of materials through chemical reactions with the environment. Common types of corrosive environments include:
Understanding the types of corrosion is essential to selecting the right fasteners. Common types include:
Choosing the right material is the first line of defense against corrosion. Here are some common materials used for fasteners in corrosive environments:
Stainless Steel: Offers excellent corrosion resistance due to the presence of chromium, which forms a protective oxide layer.
Monel: A nickel-copper alloy with superior resistance to seawater and steam at high temperatures.
Titanium: Extremely corrosion-resistant and lightweight.
Inconel: Nickel-chromium alloys that resist oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures.
Brass and Bronze: Offer good corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments.
Beyond material choice, protective coatings can significantly enhance the corrosion resistance of fasteners. Common coatings include:

While corrosion-resistant fasteners can be more expensive, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and longer service life often justify the initial investment. Balance the upfront cost with the potential costs of failure, including repairs, downtime, and safety hazards.
In marine applications, fasteners are continuously exposed to saltwater, which is highly corrosive. Here, 316 stainless steel fasteners are the preferred choice due to their superior resistance to chloride corrosion. For extreme cases, titanium fasteners may be used for their exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, albeit at a higher cost.
Industrial environments often involve exposure to a variety of chemicals and gases. For instance, in a chemical processing plant, fasteners made from Monel or Inconel are ideal due to their ability to withstand harsh chemicals and high temperatures. In less demanding industrial settings, galvanized or zinc-plated fasteners may suffice.
In agriculture, fasteners are exposed to fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste, all of which can be corrosive. 304 stainless steel fasteners are commonly used due to their good balance of corrosion resistance and cost. For more aggressive environments, 316 stainless steel or even Monel fasteners might be necessary.
Choosing the right fasteners for corrosive environments requires a thorough understanding of the environmental conditions, the types of corrosion, and the materials and coatings available. You can significantly increase the durability and reliability of your fasteners by choosing appropriate materials, such as stainless steel, Monel, titanium, or Inconel, as well as by applying protective coatings.
Having a good understanding of the requirements of your application and balancing the costs with the long-term benefits will help keep your structures and equipment safe. A regular maintenance and inspection program ensures your project’s longevity and integrity by preventing potential failures.
The right fasteners for corrosive environments can reduce maintenance, increase safety, and save you money in the long run. You will realize better performance and longevity from your installations whether they are for marine, industrial, agricultural, or architectural applications.
You can ensure the longevity of your projects by following these guidelines for selecting fasteners that can withstand the harshest conditions. Choosing the right fasteners in corrosive environments is crucial to maintaining the integrity and safety of your structures.
As always, thank you for checking out our blog. We hope that this helps you with your project.
Please also check out the other articles in our helpful guide series. We have written about Marine-Grade Metals and the Difference Between a Dome Nut and a Nyloc Nut? recently to name but two of our articles.
We are also proud to sell this product on our highly popular eBay store, check us out there too.
If you have any further questions, feel free to contact us.












Speciality Metals
Unit 1, Farrell Street, Warrington,
Cheshire, WA1 2WW, United Kingdom
Quick Links
Payment Options
